P-value Sociology Definition
In addition sociology can be defined as the scientific study of the dynamics of society and their intricate connection to patterns of. 2001One startling conclusion from this line of research is the frequency with which discrimination is reported.
Smalls definition General Sociology p.

P-value sociology definition. Critical sociology therefore rejects the notion of a value-free social science but does not thereby become a moral exercise or an individual subjective value preference as a result. While a scientist has a moral responsibility of giving findings without any biases and prejudices. Values and Norms of Society.
Power is a key sociological concept with several meanings and considerable disagreement surrounding them. Numerous surveys have asked African Americans and other racial minorities about their experiences with discrimination in the workplace in their search for housing and in other everyday social settings Schuman et al. These things include food language clothing tools music arts customs beliefs and religion.
Absolute power corrupts absolutely While many in power have indeed become corrupted and even despotic others have used their influence to fight for injustice and to aid the oppressed. The empirical results on how values matter in the daily decisions emotions and behaviors of individuals organizations and societies are scarce. Many different things make up a societys culture.
Scientific inquiry investigation presents facts as they are. The term ethnicity may. The idea that facts should not be influenced by the researchers own beliefs is a central aspect of science and so when we say that Sociology can and should be.
Being critical in the context of sociology is about using objective empirical knowledge to assess the possibilities and barriers to improving or. A p-value is the probability of seeing a simple statistic value as extreme or more extreme than the one observed in the sample if the null hypothesis is true. In null hypothesis significance testing the p-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the results actually observed under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct.
Chical causes working together in a process of evolution and also Professor. According to Peter Worsley Values are general conceptions of the good ideas about the kind of ends that people should pursue throughout their lives and throughout the many different activities in which they engage. The society at times appears to be chaotic as when a mob riots or when there is a hysterical rush from an impending crisis.
It is none of the tasks of Sociology to point out the goodness or badness of social values and determine which values are ultimately good. Sociology has been variously defined since Auguste Comte coined the term in 1838. P is also described in terms of rejecting H0 when it is actually true however it is not a direct.
Norms refers to behaviour and attitudes which are considered normal while values are those things that people consider important to them. The term value has a meaning in sociology that is both similar to and yet distinct from the meaning assigned to it in everyday speech. The P value or calculated probability is the probability of finding the observed or more extreme results when the null hypothesis H0 of a study question is true the definition of extreme depends on how the hypothesis is being tested.
Sociology is the study of human social relationships and institutions. But soon order is restored and the society gets going. Reporting p-values of statistical tests is common practice in.
Sociology is an attempt to account for the origin growth structure and activities of society by the operation of physical vital and psy-. Conformity Conflict and Deviation in Norms. It defines what is worth having and worth striving.
A very small p-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis. Sociologys subject matter is diverse ranging from crime to religion from the family to the state from the divisions of race and social class to the shared beliefs of a common culture and from social stability to radical change in whole societies. In sociological usage values are group conceptions of the relative desirability of things.
Polygamy is good or bad love- marriage is desirable or undesirable joint family system is useful or non-useful caste system is harmful or advantageous Sociology is not concerned. In the same vein sociology of education depicts an analysis of the sociological processes involved in the educational institution. Lord Acton famously noted Power tends to corrupt.
Perceptions of Discrimination. It is in this secondary socialisation that. Functionalists believe that all members of society are socialised into these norms and values first through the family and later through institutions such as education the media and religion.
Therefore they serve as a powerful source of social integration conflict and division Thome 2015. Simply sociology is the study of human society and social problems. The approach means the application of sociology to the institution of education as a separate societal unit.
Sociology is the scientific study of social relations institutions and society Smelser 1994. Value Freedom in Social Research refers to the ability of the researcher to keep his or her own values personal political and religious from interfering with the research process. In sociology values are considered as the building blocks of societies Jaspers 2016.
We do not know the importance of values for outcomes from sociological studies but there is more empirical evidence from organizational or psychological literature. Science refers to disinterestedness. Value is an abstract generalized principle of behavior expressed in concrete form in social norms to which the members of a group feel a strong commitment.
Culture is a pattern of behavior shared by a society or group of people.

How To Find Probabilities For Z With The Z Table Normal Distribution P Value Null Hypothesis
Coefficient Of Determination Regression Analysis Coefficient Of Determination Data Science

Beliefs In Society Revisesociology

Value Neutrality Explained With Examples

Difference Between Educational Sociology And Sociology Of Education Comparison Summary Sociology What Is Sociology Psychology Notes

The T Table For The T Distribution Is Different From The Z Table For The Z Distribution Make Sure You Understand Math Methods Statistics Probability Math
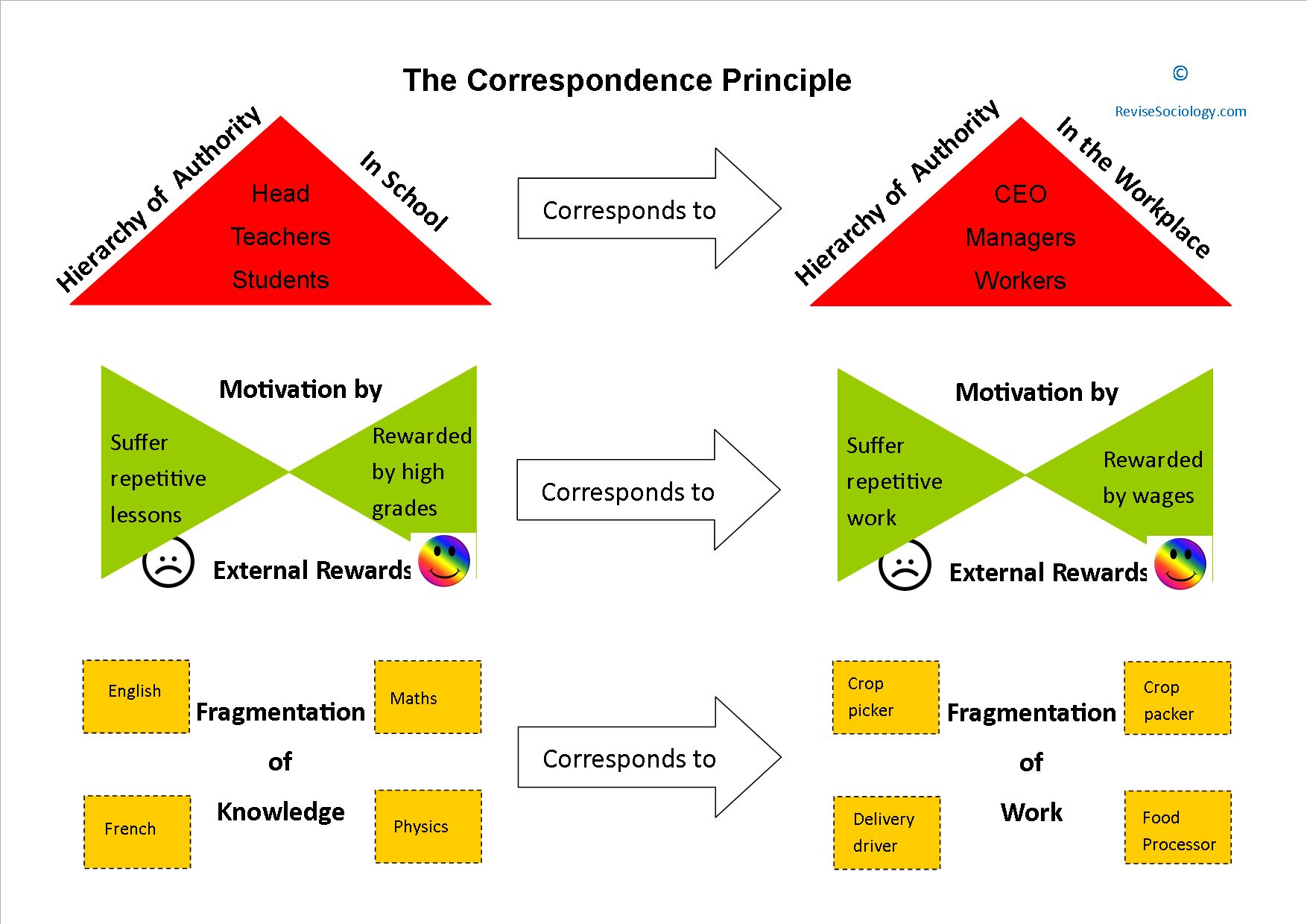
Bowles And Gintis The Correspondence Principle Revisesociology

Difference Between Role And Function Definition Characteristics Examples Leadership Management Function Role

Reading Defining The Sociological Imagination Sociology
Posting Komentar untuk "P-value Sociology Definition"